Electronics and Signal Processing
ISSN: 2959-913X (Print)
ISSN: 2959-9148 (Online)
CODEN: ESPLA8
Volumes & Issues
Contact
For any inquiries regarding journal development, the peer review process, copyright matters, or other general questions, please contact the editorial office.
Editorial Office
E-Mail: elecsigpros@elspub.com
For production or technical issues, please contact the production team.
Production Team
E-Mail: production@elspub.com
About This Journal
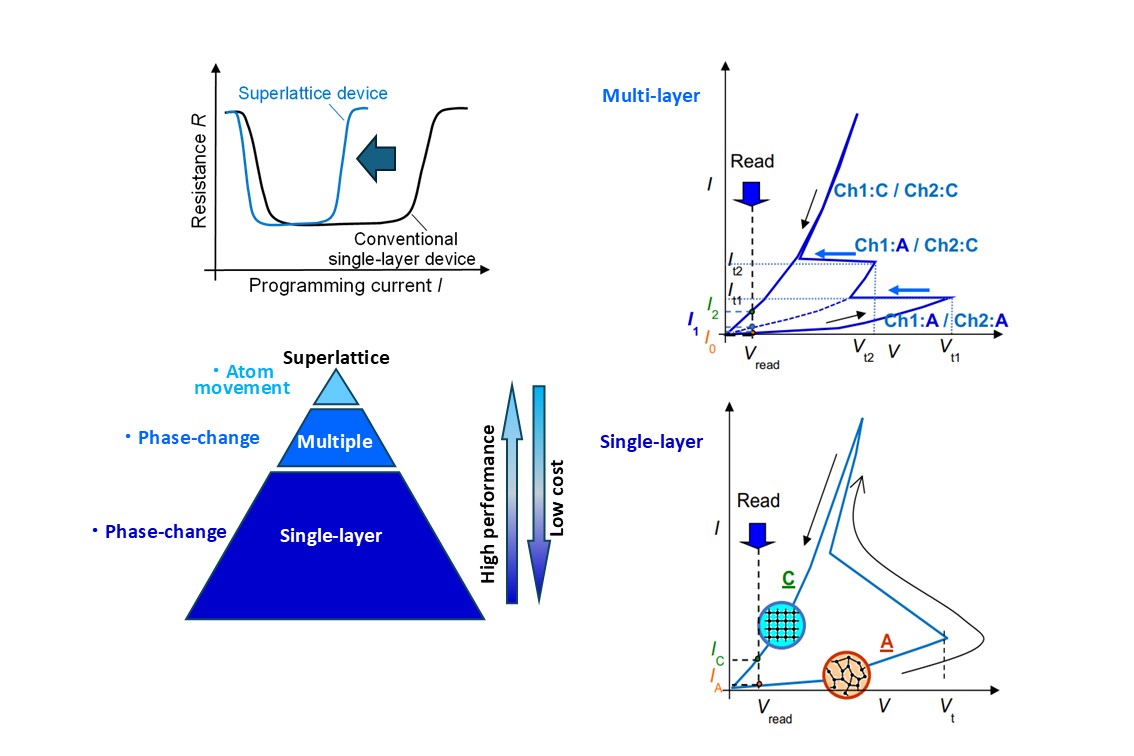
Single-layer, multi-layer and superlattice chalcogenides for non-volatile memory and artificial intelligence device
Received
14 Jan 2025
Accepted
09 Apr 2025
Published
15 May 2025
Chalcogenide materials such as GeTe, Sb2Te3, Ge2Sb2Te5, compounds of sulfur, selenium, and tellurium, are characterized by a rapid and reversible phase transition. They have emerged as versatile candidates for advanced electronic and computing applications due to their unique optical and electrical properties. The potential of single-layer, multi-layer, and superlattice chalcogenides as the active materials in non-volatile memory (NVM) and artificial intelligence (AI) devices is shown in this review. Single-layer chalcogenides often offer exceptional scalability, fast speed, and nonvolatility, enabling them usable for NVM and synaptic devices. Multi-layer chalcogenides with stacked structures exhibit unique properties different from single-layer chalcogenides, allowing high performance such as low power and multilevel storage. Superlattice chalcogenides with alternating chalcogenide layers enable ultra-low power consumption of devices, in which only few of atom moves for the operation of devices. This review also gives some related research details. A comprehensive understanding of these studies provides insights into the design and application of chalcogenide-based devices, offering pathways for future research and innovation in memory and AI hardware.
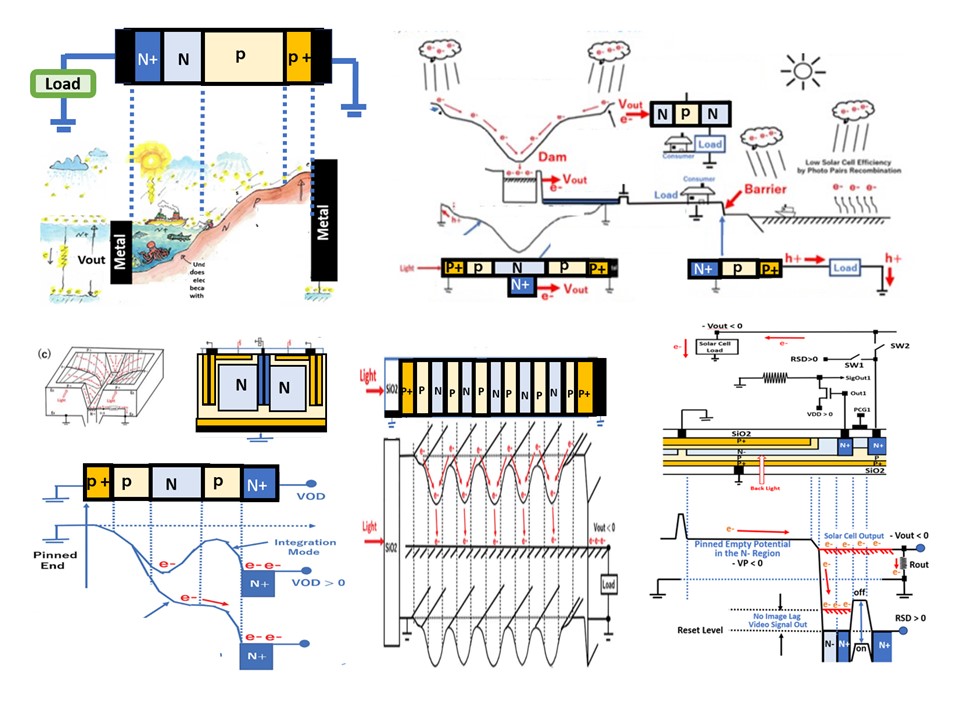
Pinned-surface and double-junction photodiode type super high-performance image sensor with built-in solar cell structure
Received
21 Oct 2024
Accepted
11 Jan 2025
Published
12 May 2025
Floating surface single-junction type photodiodes are mostly used in solar cell applications for simplicity and cost. On the other hand, pinned-surface and double-junction type photodiodes are used now in super high-performance image sensor applications. This paper first reviews the difference between the conventional floating-surface single-junction type photodiode and the pinned-surface double-junction type photodiode. The pinned-surface buried-channel P+PNPP+ double junction type photodiodes are very high-performance image sensors with no image lag and very high light sensitivity compared to conventional ones. The diode can be applied not only to image sensors but also to solar cells. In addition, this paper proposes a new AI robot vision chip in the modern 3DIC CMOS image sensor technology using this double junction type diode. So, the diode will be widely interested in process, device, and application researchers and engineers for image sensors and solar cells. A real-time AI smart robot vision chip is described as an example of application, which is composed of an array of N × N pinned-surface buried-channel P+PNPP+ double junction type photo diodes, N × N analog-data stream mask-and-match comparators, digital processing and SRAM cache buffer memory units, integrated in a 3-D multichip architecture. In the external power-off mode, the image sensor array of N × N pinned-surface buried-channel P+PNPP+ double junction type photo diodes also function as a solar cell unit for the AI self-energy robot vision chip.
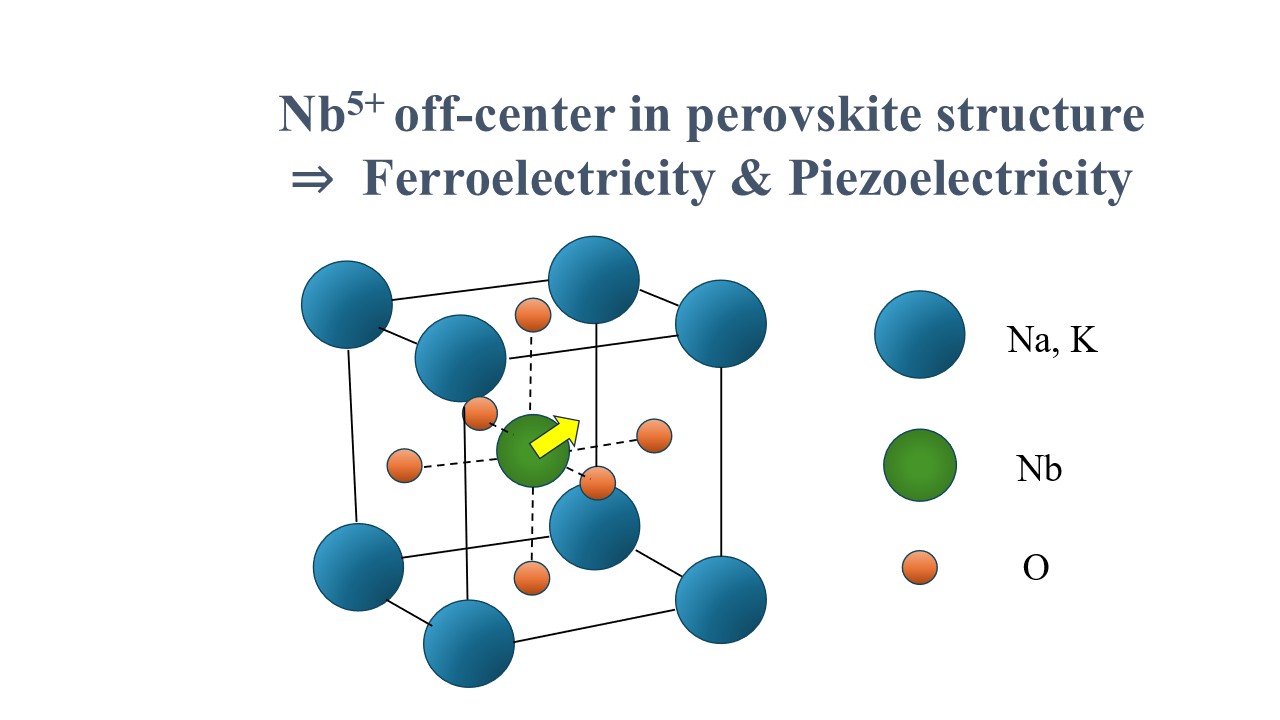
Vibrational spectroscopy of lead-free potassium sodium niobate and related perovskite ferroelectrics
Received
26 Nov 2024
Accepted
13 Feb 2025
Published
16 Apr 2025
The potassium sodium niobate (KxNa1−x)NbO3 (KNN) family with the perovskite structure is a technologically important lead-free piezoelectric material. This paper reviews the ferroelectric and structural phase transitions of KNN and related materials. The nature of end members, the physical properties, and phase transitions of simple alkali niobate materials MNbO3 (M=Li, Na, K, Rb, and Cs) are reviewed. The binary solid solution's phase diagram, KNN, is introduced concerning the morphotropic phase boundary (MPB). To understand the phase transitions near the MPB composition, the temperature dependences of lattice dynamical properties of KNN single crystals on optical modes and acoustic modes are reviewed by Raman and Brillouin scattering studies, respectively. Physical properties and phase transitions of KNN-based solid solutions were also reviewed.
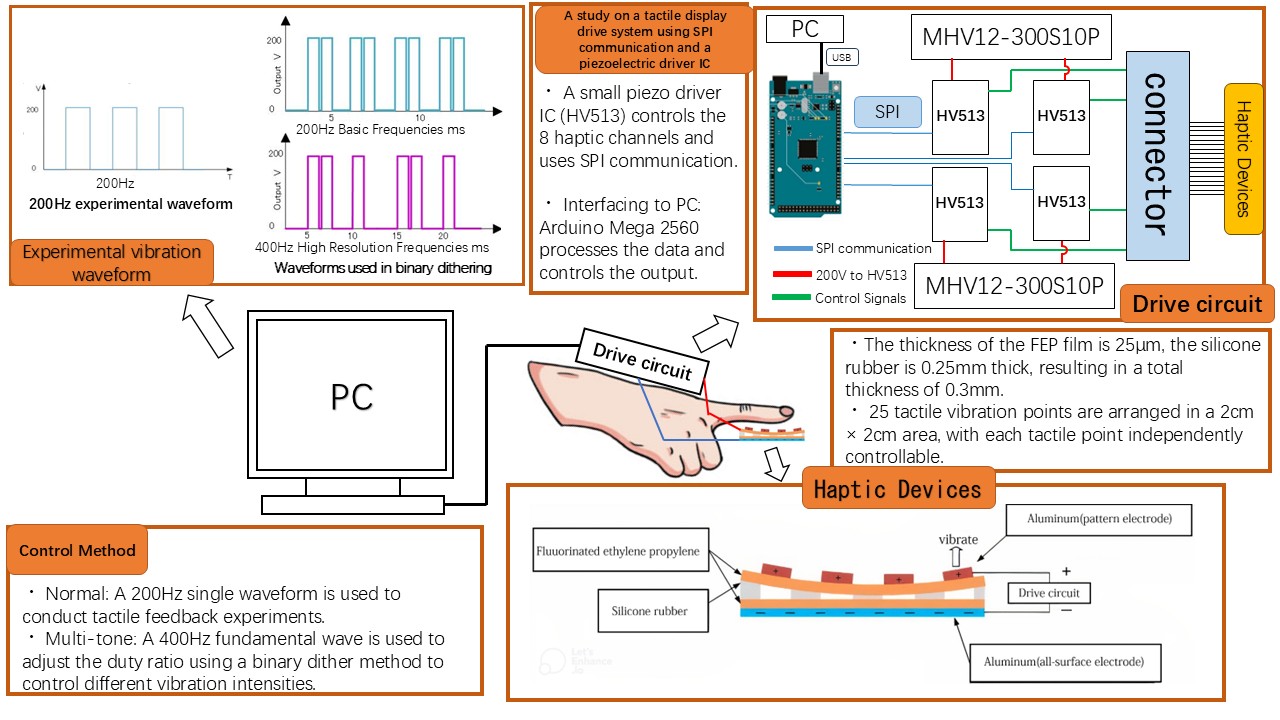
A study on a tactile display drive system using SPI communication and a piezoelectric driver IC
Received
14 Nov 2024
Accepted
17 Feb 2025
Published
17 Mar 2025
Tactile technology is becoming increasingly important due to robotics applications and the use of the metaverse. However, there is few research on tactile technologies that can provide information on two-point discrimination thresholds at the human sensory level, and practical application has not progressed. This is due to the fact that the devices are complex and cannot be compactly mounted in key locations such as fingertips. This research aims to develop thin, flexible piezoelectric resin devices and put them into practical use. Here, it is important to miniaturize the drive circuits that drive such piezoelectric devices, so we developed a drive system that uses a piezoelectric driver IC that utilizes serial communication, and is capable of generating a wide range of tactile sensations, including multi-tone gradations.
Electronics and Signal Processing — unlocking the potential of electronics and signals
Received
21 Jun 2023
Accepted
03 Jul 2023
Published
20 Jul 2023